- Startseite
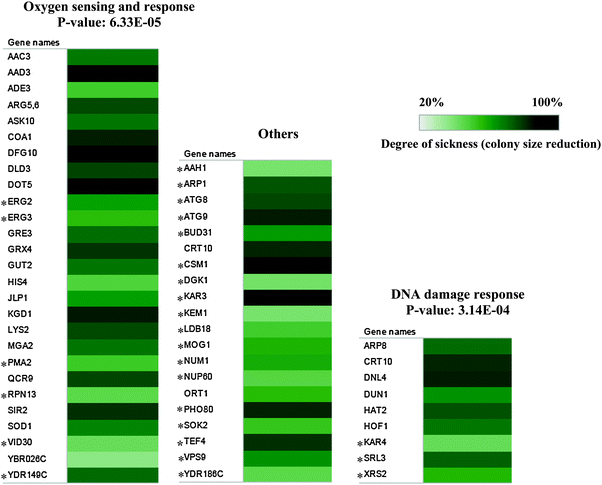
- lx arp1
- Large-scale investigation of oxygen response mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Molecular BioSystems (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C3MB25516F
Large-scale investigation of oxygen response mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Molecular BioSystems (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C3MB25516F
4.7 (407) · € 31.99 · Auf Lager

Assessing In Vivo Oxygen Dynamics Using Plant N-Terminal Degrons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae

Opposing reactions in coenzyme A metabolism sensitize Mycobacterium tuberculosis to enzyme inhibition

Analysis of the molecular basis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant with high nucleic acid content by comparative transcriptomics - ScienceDirect

Acute ethanol stress induces sumoylation of conserved chromatin structural proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae

A Genetic Toolbox for Modulating the Expression of Heterologous Genes in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803

Identification of reactive oxygen species modulator 1 (Romo 1) from black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) and deciphering its molecular characteristics, immune responses, oxidative stress modulation, and wound healing properties - ScienceDirect

Opposing reactions in coenzyme A metabolism sensitize Mycobacterium tuberculosis to enzyme inhibition
PDF) Large-scale investigation of oxygen response mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Directed Evolution Reveals Unexpected Epistatic Interactions That Alter Metabolic Regulation and Enable Anaerobic Xylose Use by Saccharomyces cerevisiae

Syk promotes phagocytosis by inducing reactive oxygen species generation and suppressing SOCS1 in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses - Young-Su Yi, Han Gyung Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Woo Seok Yang, Eunji Kim, Jae Gwang

Yeast homologs of human MCUR1 regulate mitochondrial proline metabolism

Development of conditional cell lysis mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as production hosts by modulating OCH1 and CHS3 expression

Cmr1/WDR76 defines a nuclear genotoxic stress body linking genome integrity and protein quality control

Opposing reactions in coenzyme A metabolism sensitize Mycobacterium tuberculosis to enzyme inhibition

Xylose utilization stimulates mitochondrial production of isobutanol and 2-methyl-1-butanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts